Doctors
Departments
Research Labs
Awards
Departments
MS (general surgery)
Pursuing a Master of Surgery (MS) in General Surgery is a significant achievement that opens up numerous career opportunities in the medical field. This advanced degree equips surgeons with the skills and knowledge required to perform complex surgical procedures and manage a variety of surgical conditions.
Hernia : Hernia surgery, also known as herniorrhaphy, is a procedure that involves pushing the herniated tissue back into place and repairing the weakened muscle and connective tissue
Gallbladder:The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ that stores and concentrates bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver.
Laparoscopic surgery:A surgeon inserts a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera and light, through a small incision in the abdomen. The laparoscope transmits images to a video screen in the operating room
MS (OBS Gynae)
MS in Obstetrics and Gynecology (OBGYN) is a postgraduate medical program that trains students to diagnose and treat conditions related to the female reproductive system and pregnancy
Colposcopy:A colposcopy is a procedure that allows a doctor or specialist nurse to examine the cervix in detail.
Hysteroscopy:A hysteroscopy is a procedure that allows a medical professional to examine the inside of the uterus and cervix using a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope
LEEP:LEEP, or loop electrosurgical excision procedure, is a procedure that removes abnormal tissue from the cervix using an electric current passed through a thin wire loop
MCH (Plastic Surgery)
An M.Ch. in Plastic Surgery is a three-year post-graduate degree program that provides plastic surgeons with hands-on training in aesthetic plastic surgery. The course covers topics such as
Blepharoplasty:Also known as eyelid surgery, this procedure removes excess eyelid skin or orbital fat to treat aging-related changes in the periorbital structures
Breast lift:Also known as mastopexy, this procedure enhances the shape, contour, and appearance of breasts. Breasts can sag due to a number of reasons, including age, pregnancy, weight fluctuations, genetics, and lifestyle.
Augmentation mammoplasty:This procedure enhances and enlarges breasts, and restores the shape, size, and volume of breasts that have been disfigured by medical conditions
nose reshaping:Nose reshaping, also known as rhinoplasty, is a surgical procedure that alters the shape or function of the nose
Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery is a medical specialty that treats conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and nerves. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and non-surgical methods to treat a range of conditions, including
Shoulder arthroscopy:A minimally invasive procedure for diagnosing and treating shoulder disorders
Ankle arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure for diagnosing and treating shoulder disorders
Carpal tunnel release:Carpal tunnel release is a surgical procedure that treats carpal tunnel syndrome, a painful condition that occurs when the median nerve in the wrist is compressed
Hand and wrist surgeries:Treats problems such as fractures, dislocations, and tendonitis
Urology
Urology, also known as genitourinary surgery, is a medical specialty that deals with the urinary system and reproductive organs. Urologists diagnose and treat conditions affecting these organs, which include:
kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, and male reproductive organs.
Stone removal:These include percutaneous kidney stone removal (PCNL), extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), and ureteroscopy with laser treatment
Prostate surgeries:These include prostate biopsy, transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), and transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP).
Bladder surgeries:These include reconstruction of the bladder and cystoscopy, which is a common procedure that examines the bladder lining and urethra.
Our Services
Laparoscopic Gallbladder Stone Removal
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy, also known as "keyhole" surgery, is a common procedure to remove the gallbladder and gallstones: A surgeon makes a few small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope, a thin, lighted tube with a video camera, through one of the incisions. The surgeon then uses other instruments inserted through the other incisions to remove the gallbladder. The surgeon also inflates the abdomen with gas to provide more room to work. Patients can expect to feel some pain at the incision sites and in their abdomen, and possibly in their shoulders. Pain medication, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or ibuprofen (Advil®), can help. Patients may also experience nausea or vomiting, but should feel better in a day or two
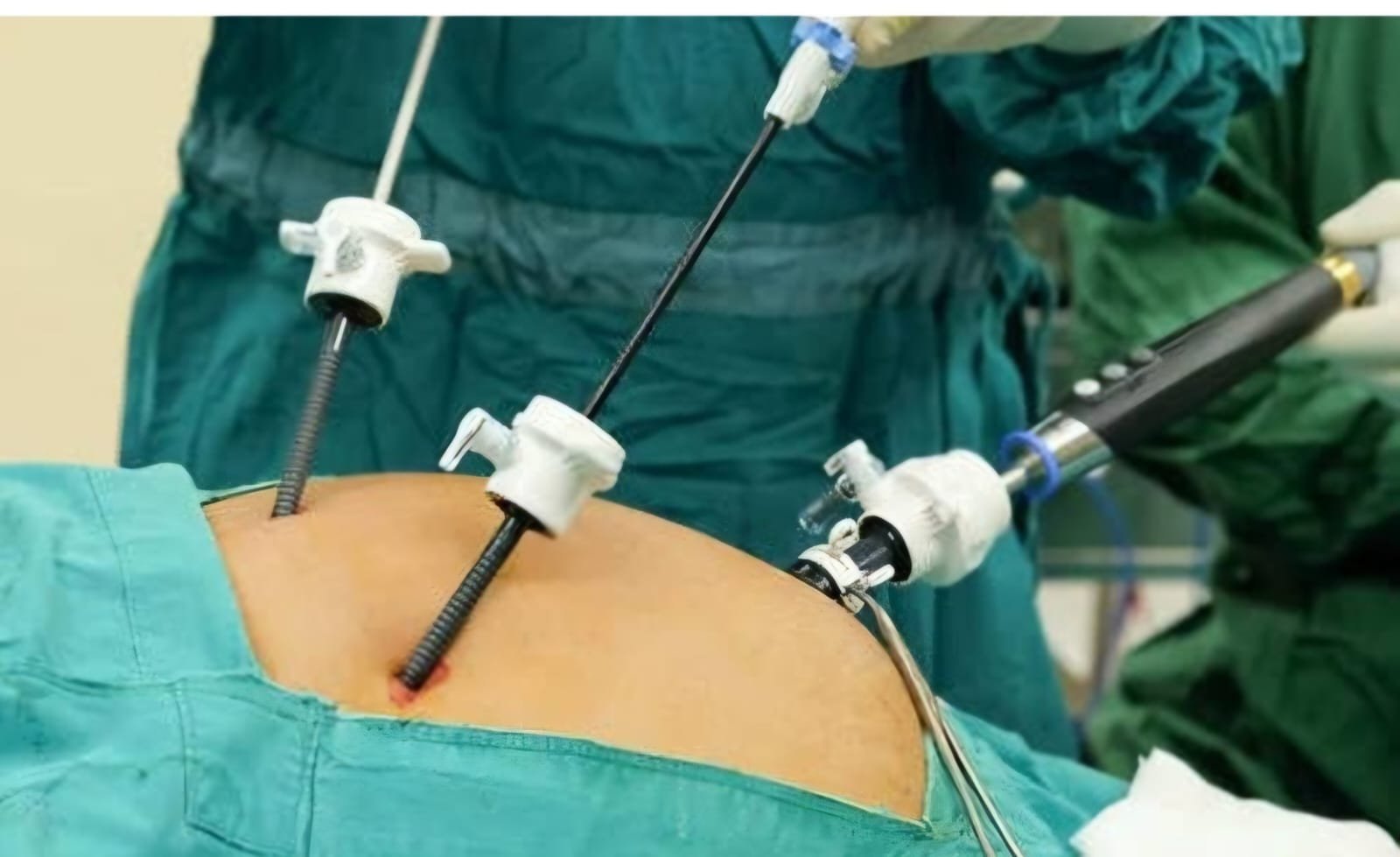
Open Gallbladder Surgery
Open gallbladder surgery, also known as an open cholecystectomy, is a procedure to remove the gallbladder through a large incision in the abdomen: While under general anesthesia, a surgeon makes a 5 to 7 inch incision in the upper right abdomen, below the ribs. The surgeon then separates the gallbladder from other organs, cuts the bile duct and blood vessels, and removes the gallbladder. The incision is closed with stitches and covered with a dressing.
After surgery, you'll usually stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days. You can expect to return to work after about 6 weeks, depending on your job and how much surgery you needed.
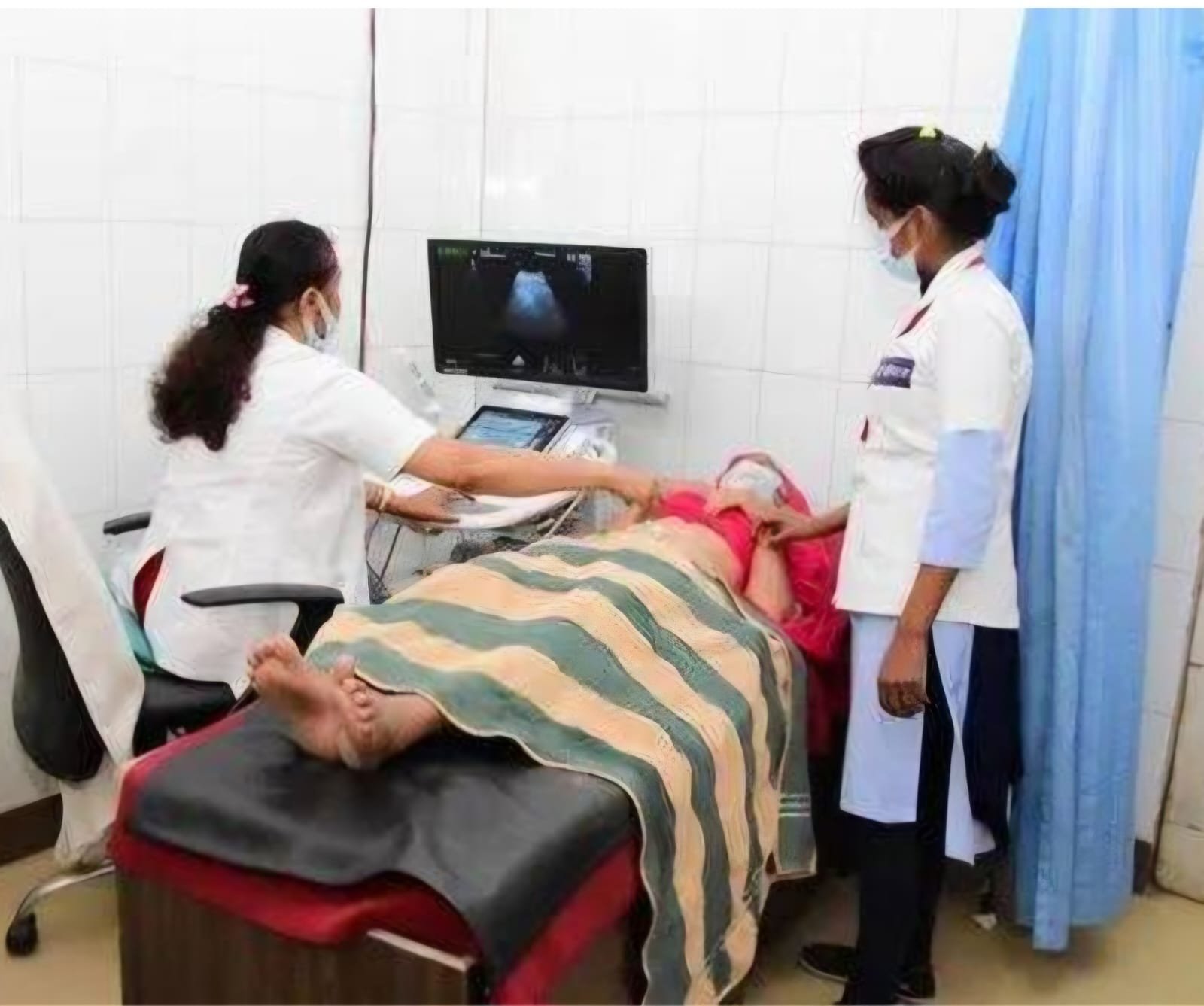
Ultrasound Service
An ultrasound, also known as ultrasonography or sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create pictures of the inside of the body
A transducer (probe) is placed on the skin or inside a body opening, and a thin layer of gel is applied to help transmit the sound waves. The sound waves bounce off the body's internal structures, and the echoes are used to create an image on a computer screen.
Ultrasounds are generally considered safe and do not involve exposure to ionizing radiation. However, unnecessary ultrasounds during pregnancy are not recommended because the long-term risks are not established.

Pathology Service
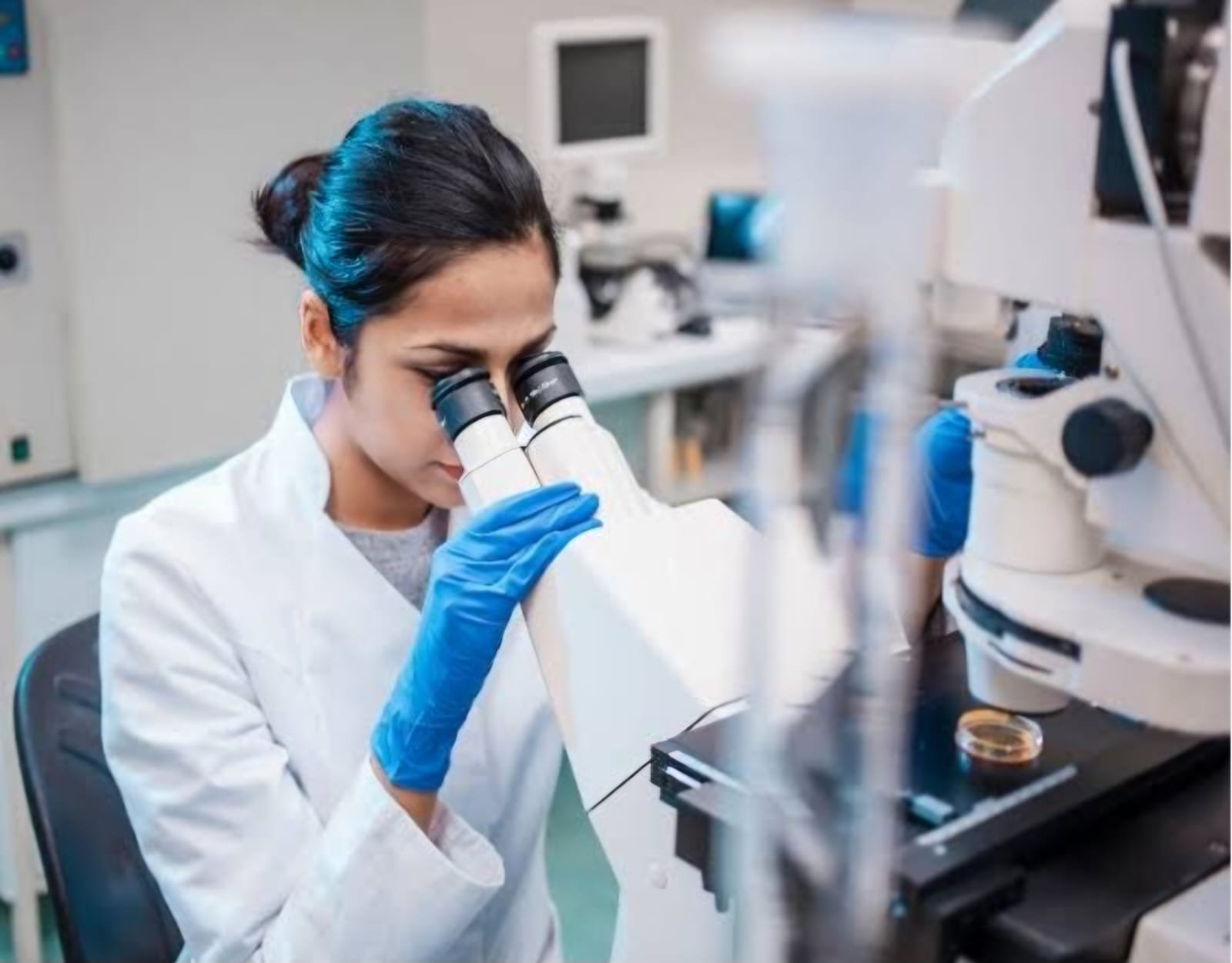
Pathology is a branch of medical science that is focused on the study and diagnosis of disease. Clinical pathology involves the examination of surgically removed organs, tissues (biopsy samples), bodily fluids, and, in some cases, the whole body (autopsy).
A pathologist studies fluids, tissues, or organs taken from the body. Pathologists often work with a surgically removed sample of diseased tissue, called a biopsy. The pathological examination of an entire body after death is called an autopsy. Pathologists are often involved in the diagnosis of illness
Pathology is the branch of medicine that deals with the study of diseases, their causes, processes, and effects on the body. It involves the examination of tissues, organs, bodily fluids, and autopsies to understand the mechanisms of disease. Pathology is fundamental in diagnosing medical conditions and guiding treatment decisions. It plays a critical role in medical research and the development of new therapies.
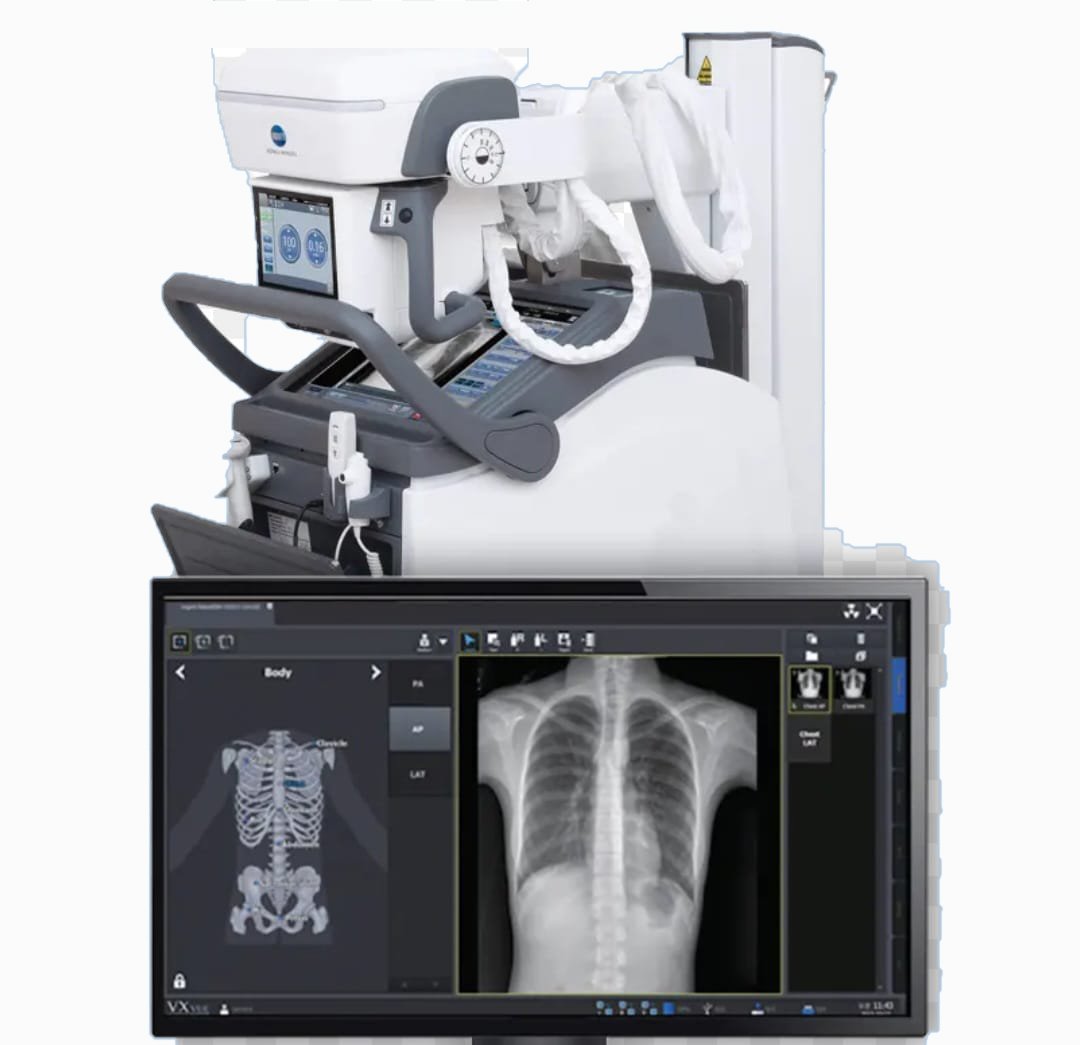
Digital Xray Service
Digital X-ray Service is a modern medical imaging technique that uses digital sensors to capture X-ray images, rather than traditional film-based methods. These images are then processed and displayed on a computer screen, allowing for faster diagnosis and improved image quality. Digital X-rays are commonly used to examine bones, teeth, and soft tissues for various medical conditions.
Key Features of Digital X-ray Services:
Faster Results: Digital images are available almost instantly, which allows healthcare providers to quickly assess and diagnose conditions.
Lower Radiation Exposure: Digital X-rays typically use less radiation than traditional film-based X-rays, reducing patient exposure while still delivering high-quality images.
High-Quality Imaging: Digital sensors produce clearer, more detailed images compared to traditional X-ray film. These images can be enhanced for better visualization of subtle issues.
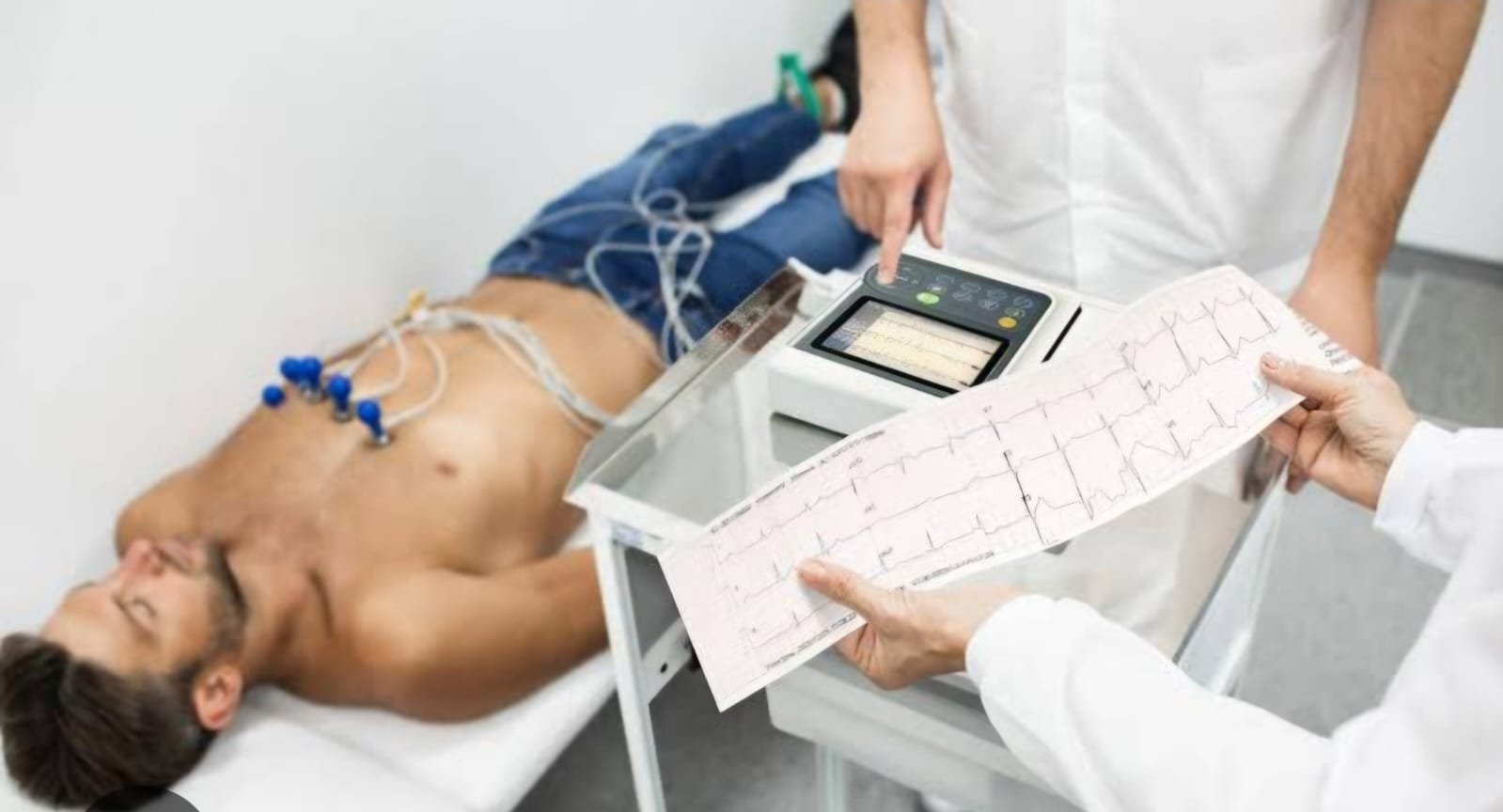
Ecg service
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive test that measures the heart's electrical activity: Electrodes are attached to the chest, arms, and legs, and connected to a machine that records the heart's electrical signals. The machine turns the signals into wavy lines that are often printed on paper. An ECG can show how fast the heart is beating, the rhythm of the heart beats, and the timing of the electrical impulses. A normal ECG shows a heart beating at a steady rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute. A doctor may recommend an ECG if you have symptoms like chest pain, breathlessness, dizziness, fainting, or palpitations. It can also help monitor how well treatments for a heart condition are working
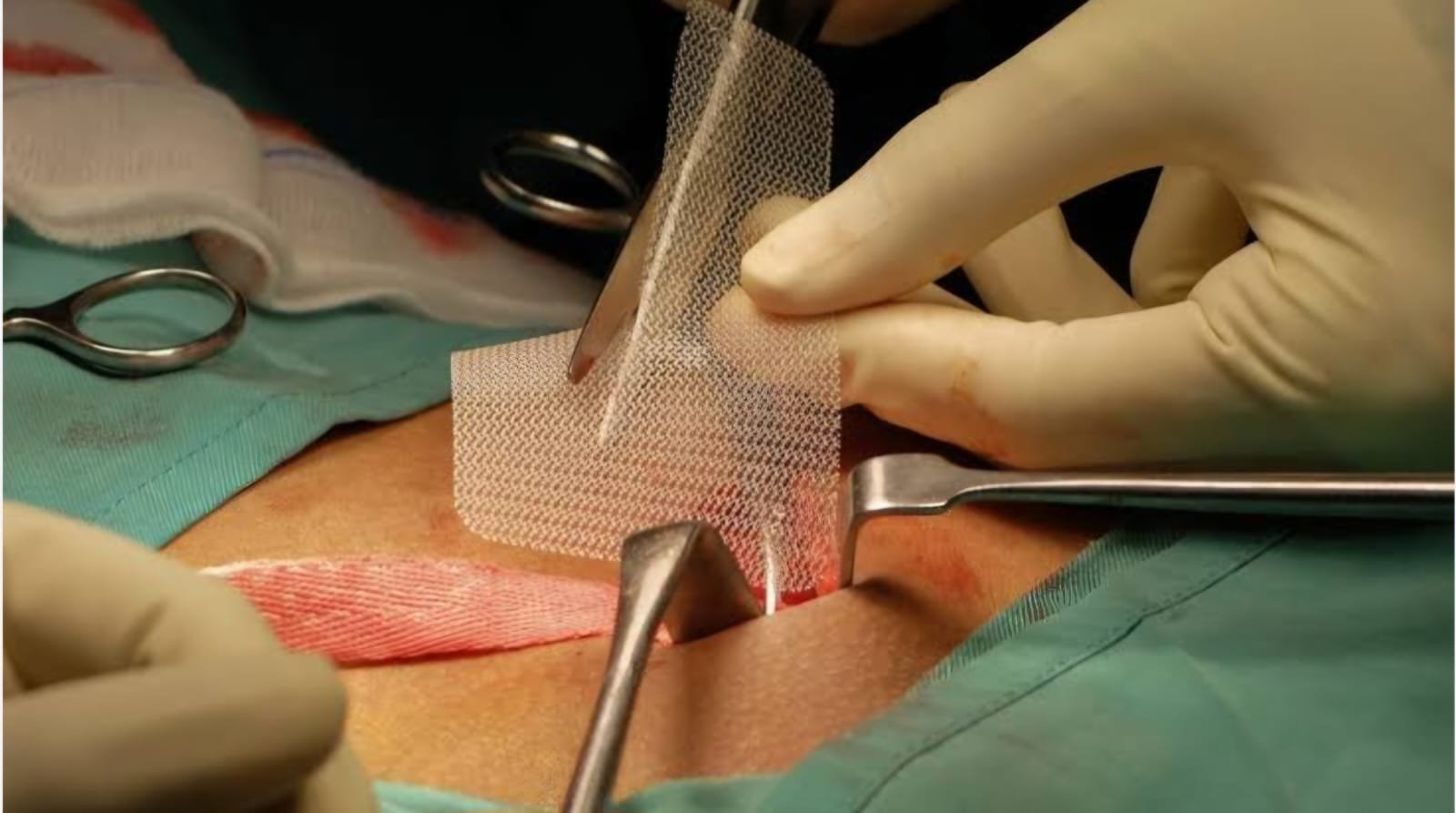
Open Surgery For Hernia
Open surgery for a hernia, also known as open inguinal hernia repair, is a surgical procedure that involves making a cut in the groin to repair a hernia: Open surgery is one of the most common surgical procedures in the world. The other main method for repairing a hernia is laparoscopic (keyhole) surgery, which is less invasive but more difficult. Most men make a full recovery from open hernia surgery, but the hernia can come back
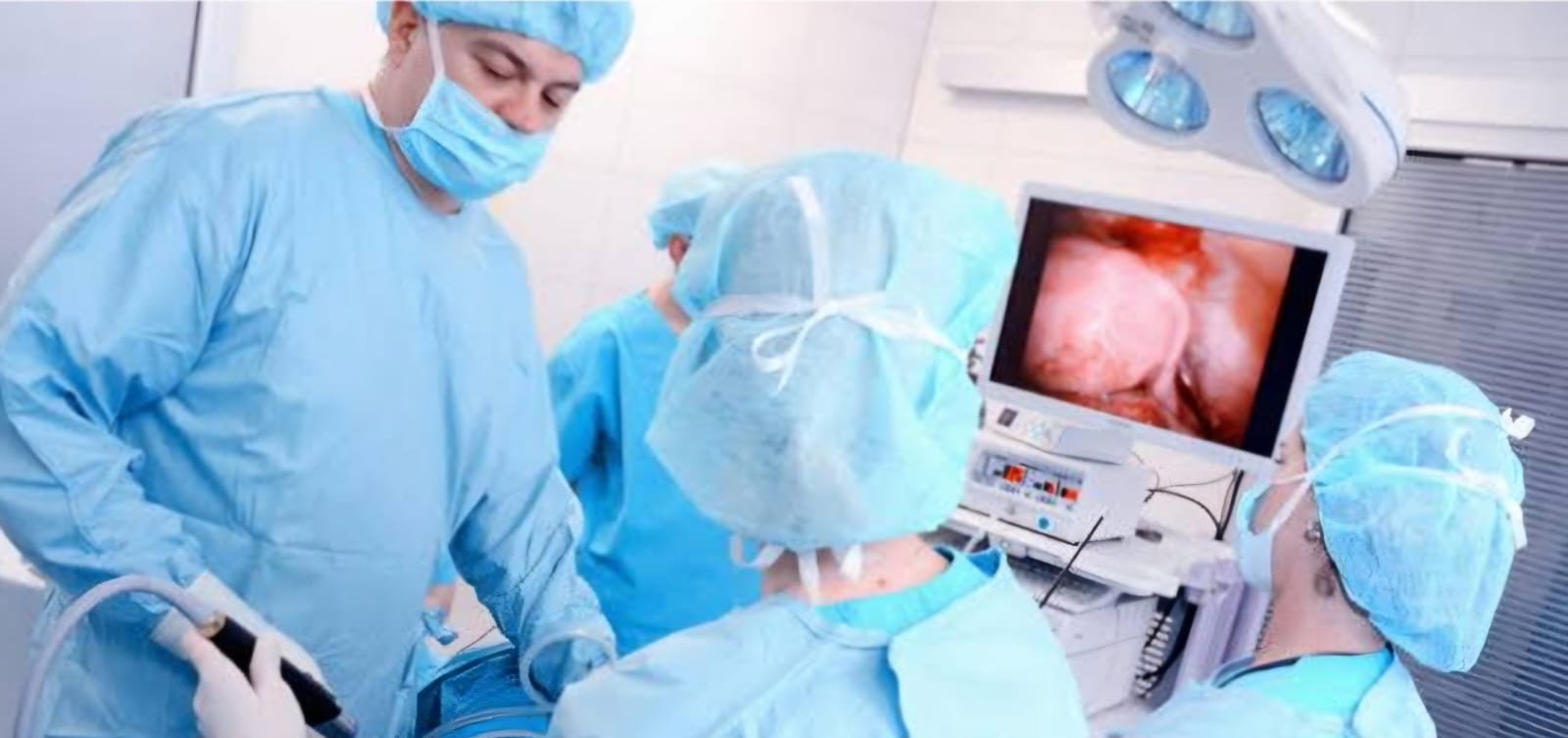
Lap Hysterectomy
A laparoscopic hysterectomy is a minimally invasive procedure to remove a uterus through small incisions in the abdomen: A surgeon inserts a thin video camera, called an endoscope, through one incision to view the pelvic organs on a monitor. Small surgical tools are used through the other incisions to remove the uterus Laparoscopic hysterectomies have several benefits, including less pain, less bleeding, less risk of infection, and a quicker return to normal activities
TURP Surgery
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure that removes excess prostate tissue to improve urine flow. It's often used to treat symptoms of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous condition that's common with aging. A transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a surgical procedure that involves cutting away a section of the prostate. The prostate is a small gland in the pelvis only found in men. It's located between the penis and bladder, and surrounds the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the penis). You'll usually stay in the hospital for 1–3 days and have a catheter in place for a few days. You can expect to recover for 4–6 weeks You should avoid lifting heavy objects or doing strenuous exercise for 3–4 weeks. You can take over-the-counter painkillers to treat pain. Drinking lots of water can help reduce the risk of a UTI and clear blood from your urine

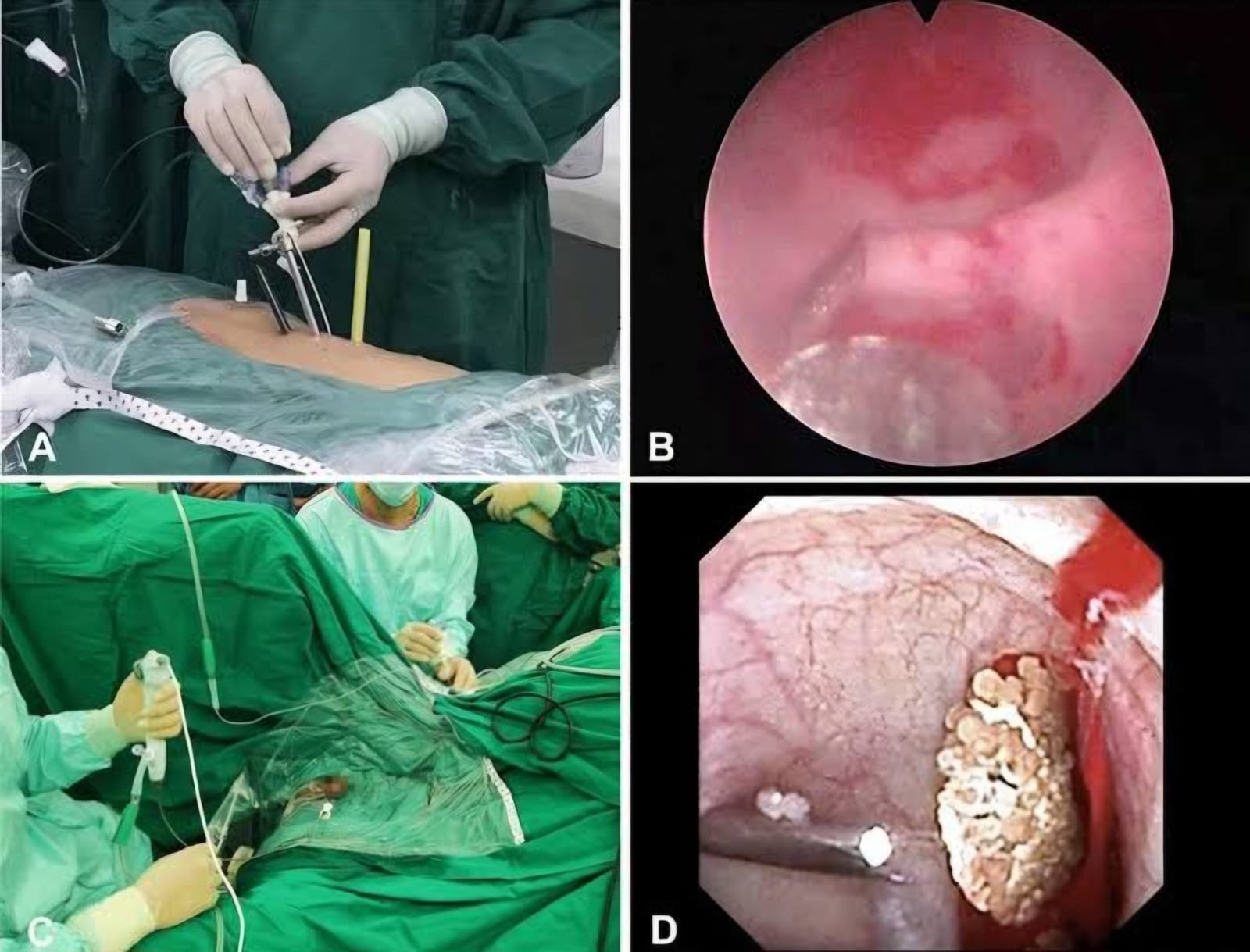
PCNL surgery for kidney stone removal
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that removes kidney stones: A urologist makes a small incision in the flank, places a tube into the kidney, and uses a telescope to locate and remove the stone. The stone can be broken into smaller pieces and removed, or it can be removed directly After the procedure, a temporary tube may be left in the kidney to drain urine. You should drink plenty of fluids and avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise for the first week PCNL is a technique used to remove certain stones in the kidney or upper ureter (the tube that drains urine from the kidney to the bladder) that are too large for other forms of stone treatment such as shock wave lithotripsy or ureteroscopy.
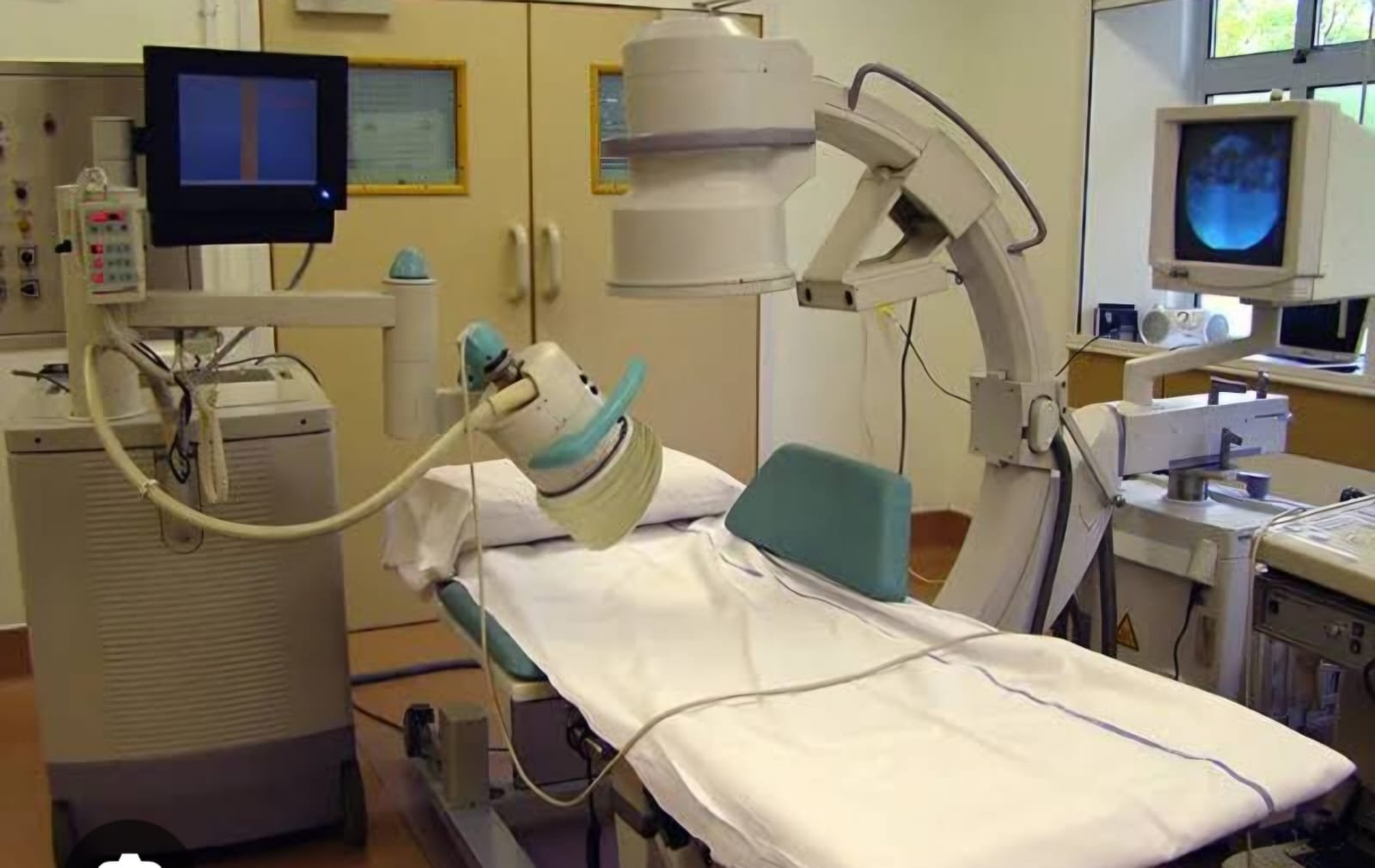
ESWL Machine For Stone Removal From Shock Wave Therapy
The machine used for extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is called a lithotripter. The lithotripter generates shock waves that are used to break up kidney stones, gallstones, or pancreatic duct stones A urologist positions the lithotripter against the patient's flank on the side of the stone An X-ray guides the lithotripter to target the stone ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that's typically performed on an outpatient basis. It's generally well-tolerated, with patients returning to normal activities within a few days ESWL is effective for small to medium-sized stones, but may not be effective for larger stones or stones with a hard composition. Other factors that can affect the success of ESWL include: